GCP Cloud Developer Certification - 01. GCP Overview
Intro
The Cloud Developer exam tests your knowledge of five subject areas:
- Designing highly scalable, available, and reliable cloud-native apps
- Building and testing apps
- Deploying apps
- Integrating GCP services
- Managing app performance monitoring
Requires familiarity with:
- Compute
- VMs
- Container clusters
- Network
- VPC
- Storage
- Cloud Storage
- NoSQL (Cloud Bigtable)
- Relational databases (Cloud SQL)
- Data warehouses (BigQuery)
Basics
- Compute offerings:
- Compute Engine
- Kubernetes Engine
- App Engine - serverless
- Cloud Run (run a single container) - serverless
- Cloud Functions - serverless
- Storage offerings
- Cloud Storage - unstructured objects (like S3 bucket)
- Filestore - traditional file sharing
- Cloud SQL
- Cloud Spanner - Massively scalable and expensive 💸
- Bigtable - analytical
- Firestore - client side webapps
- Firestore Realtime Database - sync/real time
- Memorystore - cache (like Redis?)
- BigQuery - Data Warehouse
- Networking offerings
- VPC
- VPC Network Peering - connect VPCs
- Cloud VPN - connect with on-premises
- Cloud Interconnect - connect with on-premises
- Peering - connect with on-premises
- Migration
- VMware Engine
- Migrate for Compute Engine
- Migrate for Anthos - VM to containers in GKE
- Transfer Appliance - physical data transfer
- Authentication
- Managed Service for Microsoft AD
- Cloud Identity
- AI & Machine Learning
- Sight
- Language
- Conversation
- Structured Data
- Cloud AutoML
- AI Platform
- Data Analytics
- Ingest
- Store
- Process
- Visualize
- Internet of Things
- DevOps
- Cloud Build - CI/CD
- Cloud Source Repositories - version control
- Artifact Registry - container images, dependency packages
- Global Networking
- Cloud CDN
- Cloud Load Balancing
- Cloud Armor - security, prevent DDoS
- Security
- Cloud IAM
- Key Management Service
- Secret Manager
- Data Loss Prevention
- Management Services
- Cloud Operations
- Monitoring
- Logging
- Error Reporting
- Trace
- Debugger
- Profiler
- Security Command Center
- Cloud Deployment Manager - automate creation of GCP resources
- Cloud Operations
- Regions and Zones
- a Region has several Zones
- Zone: independent part of a data center
- Interacting with GCP
- Web Console
- Google Shell
- SDK -
gcloud
For most applications you need 3 three core elements:
- Compute
- Storage
- Networking
If you have on-premises app, on your own server, you can do a "lift & shift migration". Which means taking your app to a Virtual Machine.
Compute Engine = Iaas
App Engine = PaaS
- App Engine vs. Compute Engine
- In most cases, using App Engine is a better solution than using virtual machines
- If you have an application that's not a web or mobile app, then you can't use App Engine, so you'll have to use a VM.
Cloud Run: lets you runa container using a single command.
Google Kubernetes Engine: container orchestrator (useful for apps with multiple containers)
Serverless
- App Engine - apps
- Cloud Functions - containers
- Cloud Run - functions
Cloud Function is event-driven
Storage
Cloud Storage = just like S3 buckets, non-hierarchical.
Storage classes:
- Standard
- Frequently accessed files
$$$$
- Nearline
- Files accessed about once a month or less
$$$
- Coldline
- Files accessed at most once every three months
$$
- Archive
- Files expected to access less than once a year.
$
Cloud Filestore = allows hirarchical file structure.
Filestore lets you create NFS-compatible file shares that can be mounted on your Virtual Machines or Containers.
Databases
RDBMS
Cloud SQL is a fully managed service for each of these RDB:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- SQL Server
NoSQL databases
- Bigtable
- Run large analytical workloads
- Firestore
- Build client-side mobile and web applications
- Firebase Realtime Database
- Sync data between users in real time
- Memorystore
- Speed up applications by caching frequently requested data
Cloud Spanner
Relational database and massively scalable.
💲💲💲💲💲
if your application is written specifically for a particular database, such as SQL Server, then Cloud SQL would be a better choice, unless you can rewrite it to work with Cloud Spanner.
BigQuery
If you need a Data Warehouse
BigQuery is good for aggregating data from various sources and then do SQL Queries.
Good for OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) and business intelligence reporting.
Network
VPC is very similar to an on premises network.
Each VM in a VPC can communicate to each other. You can also split VPCs into subnets and refine routes.
By default, outbound traffic to the internet is allowed. To allow inbound traffic you must define an external IP to a VM.
It's possible to connect one VPC to another one by using VPC Network Peering.
Connecting a VPC to an on-premises network:
- Cloud VPN
- Cloud Interconnect
- Peering
Using GCP Console
Ways to interact with GCP:
- Web interface (aka Console)
- SDK (gcloud, gsutil, bq, kubectl)
- Google Cloud Shell
Zones
A zone is essentially an independent part of a data center and has its own:
- power
- cooling
- network
- security infrastructure
A region has around 3 zones.
Zones are inside a region
Creating a VM
Nothing really new.
Just note that:
Spot VMs are the latest version of Preemptible VMs.
Using the CLI
# create a VM
gcloud compute instances create \
instance-name \
--zone=us-central1-a
# deploy an app using App Engine
#
# see instructions here:
# https://github.com/cloudacademy/gcp-overview#using-the-cli
#
# clone a demo app
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/python-docs-samples
# go to the directory with the app
cd python-docs-samples/appengine/standard_python3/hello_world
# deploy it to app engine
gcloud app deploy
Surprisingly, to disable the app you need to go to the App Engine through the web console.
Other Services Overview
- Migrate for Compute Engine
- Move your VMs from other Cloud Providers (or physical machines) to the Google's Compute Engine
- Migrate for Anthos
- Move from virtual machines to containers. Convert a VM into a container.
- Transfer Appliance
- Transfers huge amount of data.
- Managed Service for Microsoft Active Directory
- Cloud Identity
- AI & Machine Learning
- Sight
- Language
- Conversation
- Structured Data
- Cloud AutoML
- Data Analytics
- Ingest
- Store
- Process
- Visualize
- Cloud Composer
- Data Fusion (similar to Cloud Composer, but it's graphical/no-code)
- Internet of Things
- IoT Core
- DevOps
- Cloud Build
- Cloud CDN
- Cloud Load Balancer
- Cloud Armor
- Cloud IAM
- Cloud Key Management
Designing a Solution
Website
If you only need to set up a static website (that is, one that doesn’t have any server-side code), then believe it or not, you don’t even need to use any sort of compute service. You can just upload your website to Cloud Storage and point the DNS record for your website to it. You don’t even need to use Google’s Cloud DNS service to make this work. If your website domain is already registered with another domain registrar, then you can just update your website’s DNS record there.
More complex webapp
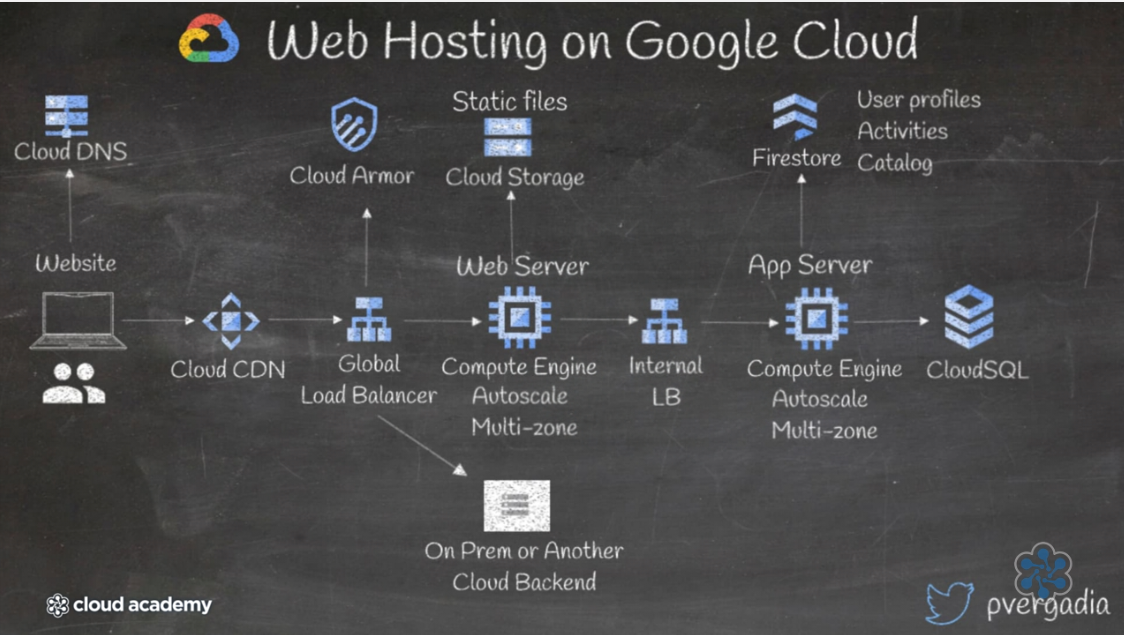
Management Services
- Cloud Operations Suite (formerly Stackdriver)
- Cloud Monitoring
- Cloud Logging
- Error Reporting
- Cloud Trace
- Cloud Debugger
- Cloud Profiler
Security Command Center
Cloud Deployment Manager:
Used when you have a resource (such as a VM) and want to deploy newly identical resources.