Core Concepts
[TOC]
Recap
Nodes
- node is a machine, physical or virtual.
- for availability we need more than one node.
- a set of nodes is a cluster
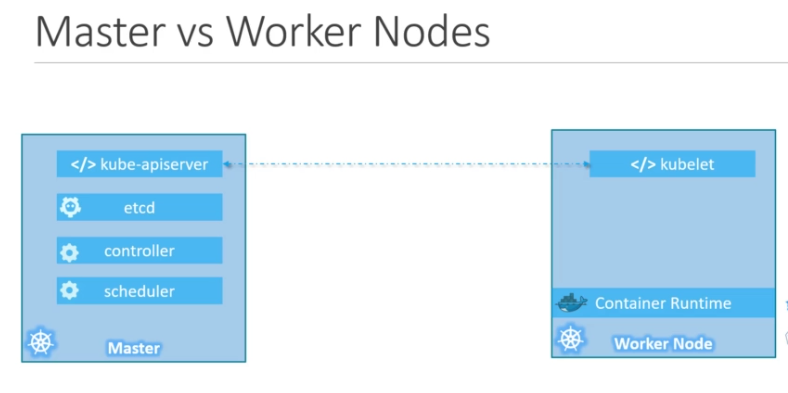
- every cluster needs a master node (responsible for orchestration) and worker nodes (responsible for actual work)
Components
Every kubernetes cluster has the following 6 components:
- API Server
- etcd
- Scheduler
- Controller
- Container Runtime
- kubelet
Brief explanation:
- API Server: acts as a frontend for kubernetes (when you use the
kubectlcommand, you're interacting with the API Server) - etcd: it's a key-value store used to store the data needed to manage the kubernetes cluster
- Scheduler: responsible to distribute work across multiple nodes.
- Controller: responsible to respond when containers/endpoints go down
- Container Runtime: underlying software responsible to run containers.
- Kubelet: an agent running on each node in the cluster, responsible to make sure the containers are running as expected.
kubectl
Used to interact with kubernetes
examples:
kubectl get-info
kubectl get nodes
Recap - Pods
A Pod is the smalles object that you can create in kubernetes.
A Pod can have one or more containers.
It's recommended to group in the same pod only containers that need to scale together.
Very minimum Pod yaml:
# example with nginx
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: container-nginx
image: nginx:1.23
Creating a Pod from CLI:
# example with nginx
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx:1.23
Recap - YAML in Kubernetes
Always present 4 top-level keys in a k8s yaml file:
apiVersion:
kind:
metadata:
spec:
Pods labs
https://kodekloud.com/topic/pods-4/
Recap - ReplicaSets
Replication Controller
The Replication Controller is responsible to respawn a new pod when the current one fails.
It can also scale the numbers of pods based on the workload, and spawn new pods on different nodes in order to distribute the workload.
Replication Controller != ReplicaSet
Replication Controller is a technology that is being replaced by ReplicaSet
yaml of a ReplicationController:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ReplicationController
metadta:
name: myapp-rc
labels:
app: myapp
type: front-end
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: myapp-pod
labels:
app: myapp
type: front-end
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-containers
image: nginx
replicas: 3
# apparently there's no 'selector'
yaml of a ReplicaSet
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadta:
name: myapp-replicaset
labels:
app: myapp
type: front-end
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: myapp-pod
labels:
app: myapp
type: front-end
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-containers
image: nginx
replicas: 3
# the difference is that a ReplicaSet definition is able
# to manage replication of pods not defined in this
# file's spec.template
selector:
matchLabels:
type: front-end
Scale
Directly from command line:
# already running ReplicaSet
kubectl scale --replicas 6 replicaset myapp-replicaset
# overwriting the value in the definition file
kubectl scale --replicas 6 -f replicaset-definition.yaml
It's recommended to change the YAML file, in order to keep the change for the future.
Recap - Deployments
Features
- deploy pods
- easily upgrade
- rolling updates
- rollback
- pause to make some changes (??)
- resume after changes (??)
Definition
same as ReplicaSet, just replace kind: ReplicaSet with kind: Deployment.
Namespaces
In the pod's definition we can set the namespace in the metadata.namespace key.
namespace definition file
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: dev
For getting info for a namespace different from the default one:
kubectl get pods --namespace=dev
kubectl get pods --namespace=prod
To change the default namespace:
kubectl config set-context \
$(kubectl config current-context) \
--namespace=dev
View pods on all namespaces:
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
I'm not really sure why in the end of the lecture the tutor showed a ResourceQuota definition file:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: compute-quota
namespace: dev
spec:
hard:
pods: "10"
requests.cpu: "4"
requests.memory: 5Gi
limits.cpu: "10"
limits.memory: 10Gi