Planning and Configuring a GCP Solution
- link to the course
- back to GCP for SysAdmins
Compute
3 main approaches to compute:
- Compute Engine (VMs)
- App Engine (Serverless - App)
- Kubernetes Engine (clusters)
Options available for specific use cases
- Cloud Functions (Serverless - standalone function, event-based)
- Cloud Run (Serverless - runs containers, invoke stateless containers using events)
Machine Types
3 main families:
- Compute Optimized
- Memory Optimized
- Sole Tenant: isolates your VMs and workloads on their own physical servers
Instances are billed based on uptime.
2 other types:
- Custom Machine Types: you can specify the amount of memory and number of vCPUs
- Preemptible VMs (aka Spot Instances): Short-lived VM instances that run for up to 24 hours at a time (not suitable for fault-tolerant workloads).
By combining custom machine types with preemptible VMs, you can really optimize costs for fault-tolerant jobs.
Important discounts:
- Committed use discounts: pay upfront for 1-3 years and get 50-70% discount.
- Sustained use discounts: kick in automatically if you run instances for a certain percentage of time over the course of a month (not applicable for App Engine flexible environment and Cloud Dataflow)
Ways to save money on GCP
- Preemptible VM
- Sustained use discounts
- Committed use discounts
Price Calculator
GCP exposes an API for querying pricing data and offers a simplified web page.
Storage
- Database
- Data stored with a certain structure
- Software accessing data
- Storage
- Generic term
- GCP has distinct offerings for simple storage
Offerings for simple storage:
- Persistent Disk Storage
- Usually attached to Compute Engine instances
- scalability and automatic encryption
- Cloud Filestore
- Network-Attached Storage (NAS)
- Critical thing to consider: latency
- Performance tiers:
- Standard
- Premium: offers higher read/write throughput
- Cloud Storage
- Object-Storage Systems. Work like S3 buckets
- See also GCP Cloud Developer - 01. GCP Overview#Storage.
- Cloud Storage Nearline: for data accessed relatively rarely, cheaper than regular Cloud Storage
- Cloud Storage Coldline: archival purposes, cheapest option.
- UPDATE: GCP now offers Archive Storage, which is similar to Coldline, but has lower storage costs, higher access costs, no SLA.
SQL-like:
- Cloud SQL
- Cloud Spanner: expensive, scalable, high availability
- Horizontal scaling is accomplished by adding nodes (more compute resources)
- Bigtable
- Wide column database
- Firestore
- Document database
- Memorystore
- Redis
- Firestore
- real-time syncing database
- stores data in JSON
Choosing the right storage option
Issues to keep in mind:
- What's the data model?
- Example: Relational vs. NoSQL
- Cloud SQL: if you need a robust managed relational database service.
- Cloud Spanner if you need global scalability and can tolerate a bit more latency (and high costs)
- Memorystore: redis service for ultra-low latency in-memory storage
- Cloud Firestore: document based
- Bigtable: wide column storage offering
- What are my access patterns?
- read-heavy vs. write-heavy vs. balanced
- What sort of queries to support?
- Strict SLA requiring very fast data retrieval? (Cloud SQL)
- Access from many different regions? (Cloud Spanner)
- Do we need cache?
- What is the expected amount of data now and into the foreseeable future?
- Are there any external constraints around cost, compliance, data location, etc.?
Network
Main services:
- Cloud DNS
- GCP solutions for configuring DNS records for domains that you own.
- Cloud Load Balancing
- Traffic routing layer
Network Peering Services
Peering is the process of connecting two separate networks so they can exchange traffic.
- Carrier Peering
- A service provider acts as a middleman
- GCP Direct Peering
- Creates a peering connection between your internal network and Google.
- Dedicated Interconnect Solution
- Similar to Direct Peering, however it creates a dedicated physical connection.
- GCP Partner Interconnect
- When you need a dedicated physical connection but your company's data center cannot access a GCP colocation facility.
- Similar to Carrier Peering solution, works through a thrid-party service provider.
Network Security Solutions
- Virtual Private Cloud
- Designed to protect traffic traveling between GCP and some other endpoint.
- Cloud VPN
- A simple way of connecting an outside network to GCP endpoints.
A VPC is an isolated subset of a larger network with firewalls to block unauthorized access. Generally it is the key unit of measure for defining your application's network resources.
A GCP VPC can span multiple geographic regions. Instances in US and in Brazil can talk to each other without accessing the public internet.
Niche networking services:
- Cloud CDN
- Traffic Director (service mesh)
- Cloud Armor (DDoS prevention)
About Traffic Director:
A network traffic management tool specifically for service mesh architectures.
A service mesh is an additional software infrastructure layer that controls service-to-service communication.
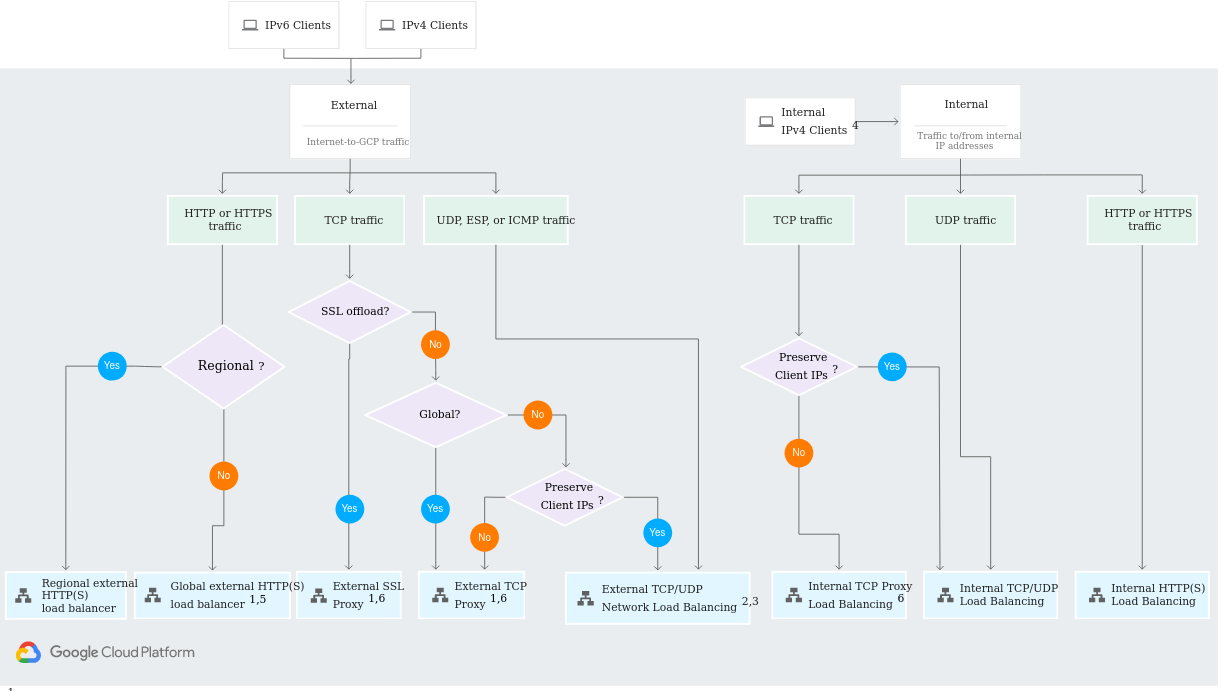
GCP Load Balancing
There are 6 types, each designed for a particular type of traffic workload. Three for global distribution, and three for regional.
3 Global types:
- HTTP Load Balancer
- SSL Proxy
- TCP Proxy: connections that are not SSL and not HTTP (note: doesn't preserve client IP addresses).
3 Regional types:
- Network TCP/UDP Load Balancer
- Used for external traffic.
- 2 specific scenarios where it's the best choice:
- you need to load balance UDP traffic
- you are load balancing TCP traffic and need to preserve client IP addresses.
- Internal HTTP(S) Load Balancer: non-accessible from public internet
- Internal TCP/UDP Load Balancer: non-accessible from public internet
Cloud DNS
DNS providers let you publish domain names and route traffic to specific servers and infrastructure.
Start by creating managed zones within Cloud DNS:
- Public Zones
- Private Zones